Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease. Occurs when the immune system fails. The development of the disease is divided into clear stages-emergence, development, stabilization and regression. The different stages of psoriasis differ in the appearance of spots and rashes, itching and soreness, and extensive skin inflammation.
Why is it necessary to distinguish the developmental stages of the disease, and what are the characteristics of the course of psoriasis in the early development and recovery process?
Why you need to understand the stages of psoriasis
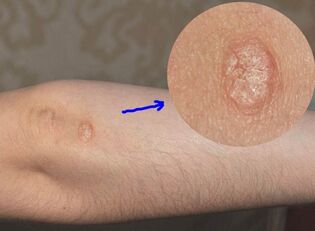
Psoriasis is divided into multiple stages and is used by doctors to choose the right treatment. The combination of drugs prescribed to treat inflammation and external drugs depends on the stage of development of the disease. At the beginning of the manifestation of the disease, conventional treatment-vitamin complex, diet, external sterile treatment of the rash, for example, UV treatment is required. Some drugs that stimulate the intestines, blood vessels, and liver are also prescribed. Ensure that the neuropathologist or psychologist corrects the emotional state of mind.
In the initial stages of the disease, they do not use effective drugs that weaken the immune system, nor do they prescribe hormonal ointments. These drugs have a large number of side effects, so they can only be prescribed without drugs.
Psoriasis: treatment in the acute and remission phases
In the case of acute progressive diseases of the disease, several drugs with multiple effects need to be prescribed. Immunosuppressants and glucocorticoids are commonly used to relieve inflammation and reduce itching. External treatment is supplemented by photochemistry, ultrasound and laser treatment. In addition, prescription drugs for the disinfection of damaged skin have been prescribed.
In a stable state, they continue to take anti-inflammatory hormone drugs and gradually reduce the dose. In order to restore damaged skin, ointments with regenerative effects are prescribed.
Relief-support the body. Correct nutrition and take a complex of vitamins and minerals to restore immunity.
Timeliness of treatment
The sooner you start treatment, the easier it will be to control psoriasis. Timely treatment limits the spread of skin inflammation, reduces the degree of inflammation, and prevents subsequent recurrence of peeling. Since psoriasis is often mistaken for an allergic rash at an early stage, it is necessary to know its initial symptoms so as not to miss the appearance of the skin disease.
Note: Doctors are still studying the cause of psoriasis. However, it is well known that the skin inflammation of psoriasis is not contagious. It cannot be removed from the patient, nor can it be infected while injured. This is our own failure in the human body.
Psoriasis is caused by immune failure, which may be caused by many factors. Severe stress, poisoning (including potent drugs, industrial emissions, alcohol), previous infections.
Psoriasis is difficult to treat. The disease is easy to relapse and relapse. And the treatment itself is symptomatic treatment. It prevents the appearance of new spots and relieves existing skin itching.
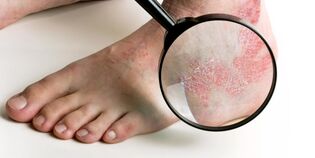
Which stage of psoriasis is called the initial stage? How to distinguish early psoriasis and quality rash? How will the disease develop in the future?
Psoriasis: Early stage
The first appearance of psoriasis on the skin looks like a papule. The rash is most common in the bends of the elbows and knees, or where clothes are tightly pressed against the body (for example, under the belt at the waist). A rash can also appear along the edges of the hair and under the hair, around the nails and on the nail plate. Sometimes psoriasis can occur on the feet and palms.
Psoriasis almost always appears symmetrically-on the elbows of both hands, on the sides of the lower back, or on both knees. The pimples themselves (pimples in medical terms) have a moderate appearance in the early stages. They have:
- pink or red;
- The sharp edges are blurred;
- Small size-papules on the bottom do not exceed 2 mm;
- Flat shape-the small punctate papules at the beginning of the disease are hardly raised, so they look like spots.
As the disease progresses, peeling scales will appear on the papules. They are gray or silver, and they look white against the background of red pimples.
The appearance of scales is accompanied by severe itching. If you don't resist and scratch, then remove the scales, revealing the shiny areas of pink youthful skin underneath. It is very thin, fragile, and prolonged scratching itchy papules-wounds, bleeding.
The initial stage of psoriasis lasts up to 4 weeks.
Psoriasis: Progressive stage
In the developmental stage, the various papules merge into a common spot, forming the so-called psoriasis plaque. They grow above the surface of the skin and are almost completely covered by scales. There is a non-flaking pink-red edge on the edge of the psoriasis plaque.
The presence of edges is a sign of the stage of disease progression. The rim width is 1-2 mm. Its skin is inflamed and its structure resembles parchment paper.
The edge represents the extended area of the point. This is skin that has been inflamed but has not yet peeled off. After a while, it will also be covered with scales. And the patch will expand to cover the new area of the skin and form a new wider edge.
As the disease progresses, adjacent spots merge with each other. At some point, a large erythema may form on the human body.
The psoriasis plaques are very itchy, giving people an unpleasant feeling, and ruining his work, rest and sleep. They will grow up, occupy a large area, and form a new rash on clean, healthy skin.
The main sign of an advanced stage is the appearance of a new rash. Once new papules and spots appear, the next stage of psoriasis begins-static. This is not a complete victory, but it is already in the direction of recovery.
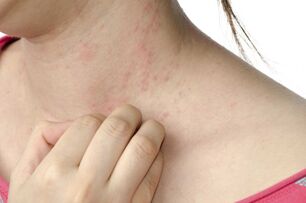
In the developmental stage, psoriasis is almost always accompanied by weakness, fatigue, and weakness. Depression is very common. Temperature possible.
The progression of psoriasis can last as long as several months.
Psoriasis: stable phase
The main sign of the stationary phase is to stop the appearance of new spots and rashes. At the same time, the itching is also reduced and becomes easier to bear. The rash loses its bright color, changes color, and becomes invisible. This is also one of the signs that the process is stabilizing.
When the inflammation stops spreading, the pink band around the plaque disappears. Start active exfoliation and healing, regenerating new healthy skin.
It can be seen to the naked eye that peeling at the fixed stage has increased. The scales completely cover the entire surface of the psoriasis spots, and there is no room for the rim. Psoriasis has a typical flaky appearance, which is generally recognized by the public.
There is no danger of extensive peeling during the fixation phase. When all dead cells fall off the surface of the psoriasis spots, healthy skin with a slight shadow will remain in place.
Other signs of progress or stability
In addition to the appearance of rashes, spots and scales, there are many other signs that can be used to judge the development of the disease. This is the itch (strong or tolerable), general condition, and the essence of depression. There is also temperature.
In the initial stage, itching is variable and the rash is difficult to understand. In addition, itching is getting worse every day. In the acute phase of psoriasis, it becomes unbearable. Interfere with sleep, rest, and work. The person became irritable because the itching sensation did not give him a chance to rest.
In the plateau phase, the itching subsides. Everyday-one feels better. General changes in mental state, negative emotions and depression will weaken. The duration of the fixed phase is a few weeks-from 2 to 5.
Psoriasis is in decline
The fading stage of psoriasis is the almost complete disappearance of plaques, spots, redness, inflammation, and itching. At this stage of the disease, only the different pigmentation of the skin is reminiscent of psoriasis. Instead of the previous psoriasis spots, it looks lighter. The surface of healthy skin has a darker shade.
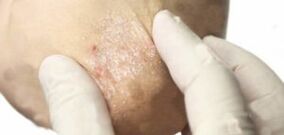
In some cases, so-called hyperpigmentation develops. The skin at the psoriasis spots does not lighten, but darkens. In any case, the difference in skin pigmentation will continue for one to two months.
After recovery from psoriasis: the possibility of recurrence
The possibility of recurrence of psoriasis depends on the person's lifestyle, diet, allergic mood, and overall physical condition. It also depends on the toxin content in his body, blood, and liver. If you strengthen the immune system and cleanse the liver, blood vessels, and intestinal toxins, you can reduce the possibility of repeated skin inflammation.
Psoriasis usually rarely recurs seasonally after washing. A person is still susceptible to illness, but the probability of its occurrence is significantly reduced.
Cleanse toxins in the body and take vitamin and mineral complexes to help strengthen immunity. This is especially important if immunosuppressants are used during the treatment of advanced psoriasis. Their needs are due to the work of inflammatory mediators. After suppressing the autoimmune defenses, it is necessary to restore the immune system.
Clinical manifestations
At the onset of the disease, in most cases, the rash is limited and expressed as a single plaque on its favorite location (scalp, elbow extensor surface, knee joint, bone, etc. ).
The plaques are clearly demarcated from healthy skin (bright pink or deep red), covered with loose silvery white scales. Scratching can produce psoriasis-specific triad phenomenon-"scleroderma", "final"Film", "blood dew". . .
Psoriasis has 3 clinical stages: progressive, static and regressive.
Classification
Depends on the degree of the inflammatory process, the main part of the rash, the severity of the patient's condition and other clinical signs, common plaque psoriasis, exudative, arthropathy, pustular, psoriatic redDermatosis, folding psoriasis, palm and sole psoriasis. It should be noted that a patient may have different clinical variations at the same time.
Exudative psoriasis is characterized by a marked inflammation of the skin, which is manifested by the presence of a layered scaly crust on the surface of the plaque, sometimes multi-layered, with an appearance similar to puff cake (in this case, this form of psoriasisCalled the class rupee). When the scaly crust is removed, a permeable surface is exposed.
Clinically, in addition to the usual plaque outbreaks, arthritic psoriasis also has joint disease, which is usually small, distal, and rarely large.Arthritis may occur before skin lesions are present or before skin lesions. Psoriatic arthritis manifests as pain, swelling, and varying degrees of restricted mobility of the affected joints, ranging from mild joint pain in a single joint to systemic pathology and patient disability. Patients with severe skin manifestations (psoriatic erythroderma, pustular psoriasis) are more likely to develop articular psoriasis, but the combination of severe joint damage and relatively limited rash is also possible.
Pustular psoriasis can be generalized (Tsumbusha) and limited by it, accompanied by palms and soles (Barbera). Stressful situations, infections, unreasonable routine or topical treatments lead to the appearance of this severe form of psoriasis.
Systemic pustular psoriasis will have fever, leukocytosis, increased ESR and general serious conditions. Suddenly, against the background of bright erythema, shallow pustules appeared, accompanied by burning pain, soreness, and they can be located on the normal plaque area as well as the previously unchanged skin. The new pustular lesions appear paroxysmal and occupy most of the skin. The combined pustules cause epidermal shedding in the form of "purulent lakes" and may develop erythroderma.
Pustular psoriasis is more common. The rash mainly appears on the palms and soles of the hands in the form of pustules, with erythema and skin infiltration as the background. Compared with the general situation, the course of the disease is mild and the general situation is satisfactory, but it persists and relapses frequently. Irritating topical therapy is a predisposing factor.
Psoriatic erythroderma is a serious form of psoriasis. With the gradual development of the psoriasis process and the fusion of dental plaque components, it gradually develops into the exhaustion of the entire skin, which is characterized by sharp congestion, edema, and skinInfiltration, with a large number of large and small flaky cells, peeling of psoriasis rarely occurs. Subjective-itching often. The disease can start with erythroderma. General conditions will get worse (fever, weakness, lymph node reaction, heart failure, impaired liver and kidney function, changes in blood tests, hair loss, etc. ).
Folded psoriasis is more common in children and the elderly, especially in diabetic patients. The lesion is located in the armpits, under the breast, in the perineum, in the groin folds, and in the belly button, and has a sharp border, saturated red color and slight peeling.
Psoriasis on the palms and soles of the feet can exist alone or at the same time as damage to other parts of the skin; the typical psoriasis triad is difficult to cause.
Three clinical stages of psoriasis
In progress. Under the influence of irritating factors (trauma, psychological stress, infectious diseases, insufficient treatment methods, etc. ), the deterioration of the disease may appear with the appearance of a large number of small nodules, which are easy to grow around and form various sizesAnd contour patches, these patches can be separated or separated. It occupies a large area of the skin until general skin lesions.
In the advanced stage, it is characterized by symptoms of isomorphic reaction (Keberner phenomenon), which is characterized by a typical psoriasis outbreak occurring in the injured area, or even in the minor area.
Fixed stage. In the stationary phase, the emergence of new elements ceases and the peripheral growth trend of existing patches disappears.
The return stage. The degenerative phase is characterized by reduced intensity of the color of the plaque, flattening, reduced peeling, infiltration, reduced element absorption, and subsequent formation of hypopigmented or hyperpigmented lesions in the previous rash.
Treatment
For mild, limited manifestations of psoriasis, topical external treatment in the form of salicylic acid ointment, naphthalene preparations, tar or emollient ointment is sufficient. Severe disease forms require complex systemic treatments using detoxification, desensitization, different groups of anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy methods, topical drugs, etc.
This section will introduce the available methods and the most modern effective methods for psoriasis treatment.
Systemic therapy
The management of patients at different stages of the psoriasis process is unique. Late treatment requires special care. During this period, hemodez was required to instill 30% intravenously. Sodium thiosulfate solution i/v, 10% calcium gluconate solution, with high blood pressure, it is recommended to introduce magnesium sulfate solution. Use moisturizer or 1-2% externally. Salicylic acid ointment.
Aromatic retinol.Acitretin (neotigazone)-a representative of the second generation of monoaromatic retinoids, used to treat severe psoriasis, with a daily dose of 10 to 20-30 mg, depending on the severity of the skin process. The mechanism of Acitretin is to inhibit the proliferation of epidermal cells and normalize the keratinization process. The drug is particularly effective in combination with PUVA therapy. When prescribing Acitretin, don't forget its teratogenic effects.
Cell inhibitors.Methotrexate is used for persistent psoriasis and contraindications to other treatments. It is a folic acid antagonist and mainly acts on actively proliferating cells. Very toxic. There are many methods of administration, and it is best to administer intramuscularly once a week under strict laboratory control.
Immunosuppressant.If there is severe generalized psoriasis resistant to other therapies, cyclosporin A should be prescribed. The drug has an immunosuppressive effect, has an inhibitory effect on cell growth, and can inhibit the secretion of cytokine activated lymphocytes and the expression of interleukin-1 receptors on immune function cells. In psoriasis, the prescribed dose is 5 mg per kilogram of body weight per day.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugsare used for the treatment of arthritis psoriasis, and to reduce acute inflammation of exudative psoriasis and erythroderma. The daily dose of the drug and the duration of treatment depend on the intensity of the pain syndrome, the degree of inflammation and individual tolerance.
The use of systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of psoriasis is considered inappropriate, and it leads to diseases that are resistant to various types of treatments. In severe cases of arthropathic psoriasis, corticosteroids can be used for long-term intra-articular administration. The dose and duration of treatment depend on the size and degree of inflammation of the diseased joint.
Physical therapy.One of the most effective treatments is PUVA therapy or photochemotherapy (PCT). PCT is a combination of long-wave ultraviolet radiation (wavelength from 320 to 420 nm) and photosensitive furanocoumarin drugs. The use of photosensitizers is due to their ability to increase the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet light and stimulate the formation of melanin. PUVA therapy leads to inhibition of cell proliferation, inhibition of pathological keratinization, and affects the metabolism of prostaglandins and the permeability of cell membranes. The photosensitivity reaches its peak 1-3 hours after taking 8-methoxypsoralen. The weight of the patient should be considered when choosing the dose of the drug. The program is released 3-4 times a week for 20-25 times.
Local PCT can also be used with external photosensitizers.
The combined use of PUVA therapy and retinoids is called Re-PUVA therapy. In severe cases of psoriasis, its clinical effect is the highest.
Selective phototherapy (SFT)-UV radiation in the medium wave spectrum (wavelength 280-320 nm) without taking photosensitizers. SFT is used for less obvious disease manifestations, that is, there are contraindications to the use of PUVA treatment.
How to recognize psoriasis at an early stage
The treatment of psoriasis is the most effective at the earliest stage. Therefore, timely diagnosis is very important. Only a dermatologist can tell you if you have psoriasis or other skin diseases. However, you can identify this disease yourself by several characteristics:
- Psoriasis usually first appears in the folds of the arms and legs, the hairline or where the clothing is in close contact or friction with the body-under the belt of pants, various elastic bands or belts.
- At the onset of the disease, a very itchy rash, covered with gray or silver skin scales, is easy to remove.
- Removal of scale will reveal thin, shiny and slightly moist skin.
- If you scrape the plaque with a spatula to remove the scales, the blood stain will appear on the stain in the form of tiny droplets. However, it is best not to use the latter method for self-determination of psoriasis, because this method is easy to get infected.
For complete peace of mind, you need to see a doctor, because patients themselves often confuse psoriasis with various types of lichens or allergic dermatitis and use inappropriate drugs for treatment.
What if you notice the initial symptoms of psoriasis?
Psoriasis cannot be cured once and for all, so the main goal of treatment is to obtain stable and longest relief. You should know that without proper treatment, psoriasis can quickly become a chronic disease: acute attacks can occur up to 9 times a year and last up to 15 days.
What should you do if you suspect that you have psoriasis? Usually, people who find that they have signs of this disease make a big mistake, resorting to a "cannon"-hormonal ointment (so-called topical glucocorticoid) without consulting a doctor. Often, patients explain this step by the fact that they are said to be able to help quickly when they learn from a friend of this kind of funds. This is a big mistake!
What is the danger of this self-medication? Hormonal ointments for psoriasis have many side effects and contraindications. If there is no strict advice from a doctor, please do not use them for the duration, frequency of use, range of application on the body and the individual characteristics of your body, which are very undesirable.
Non-hormonal drugs such as zinc pyrithione should be used to effectively treat early psoriasis. Zinc pyrithione or active zinc is a very effective drug for the treatment of psoriasis, with complex effects:
- Inhibit excessive skin cell proliferation and inflammation, reduce scaling and the formation of psoriatic spots;
- Relieve itching;
- Protect damaged skin from bacterial and fungal infections;
- Restore the protective function of the lipid layer and skin.























